I. Oral health is an important component of overall health.
The World Health Organization lists oral health as one of the ten criteria for human health. The criteria for oral health are "clean teeth, no cavities, no pain, normal gum color, and no bleeding."
Oral health is closely linked to overall health. Infections and inflammatory factors in the mouth can cause or exacerbate chronic diseases such as cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and diabetes, endangering overall health and affecting quality of life. Caries and periodontal disease damage tooth hard tissue and surrounding supporting tissues, not only affecting functions such as chewing, speech, and aesthetics, but also causing social difficulties and psychological impairments. Oral infections in pregnant women are a risk factor for premature birth and low birth weight.
Some systemic diseases may manifest in the oral cavity. For example, patients with diabetes have reduced resistance to infection, often developing periodontitis and difficulty healing tooth extraction wounds. Early-stage AIDS patients may develop oral lesions and develop diseases such as oral candidiasis.
Maintaining oral health is an important means of preventing and controlling systemic diseases, and preventing and controlling systemic diseases contributes to promoting oral health. Oral diseases share common risk factors with chronic diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, such as smoking, alcoholism, an unhealthy diet, and mental stress.
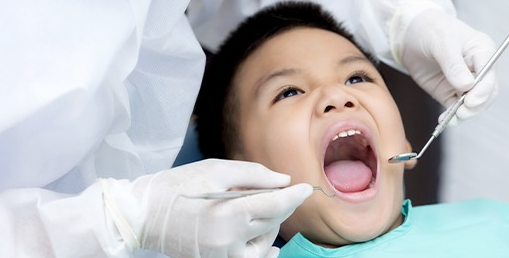
II. Oral diseases are preventable, controllable, and treatable.
Caries and periodontal disease are bacterial infections. Plaque bacteria and their products are the initiating factors for caries and periodontal disease. Without plaque microorganisms, caries and periodontal disease cannot occur.
Preventing and controlling oral diseases requires a combination of personal and professional oral care. Personal oral care includes effective toothbrushing, a balanced diet, appropriate fluoride use, and regular dental checkups; professional oral care includes topical fluoride application, pit and fissure sealants, and scaling (teeth cleaning).
Effective toothbrushing removes plaque and is the primary method of personal oral care. Adults are recommended to use a horizontal oscillating brushing technique, brushing thoroughly, focusing on removing plaque along the gum line and between teeth. Each brushing session should last at least two minutes. Children are recommended to use a circular motion. Parents can help children brush their teeth until they can fluently write Arabic numerals (ages 6-7). Dental caries and periodontal disease are both preventable and treatable. Regular checkups and early prevention are key. Early-stage dental caries can be controlled or even cured through measures like fluoride use. Early-stage gingivitis can be cured through cleaning and effective toothbrushing.
Adults are recommended to have a dental checkup every six months to a year, and children every three months to six months.